🔹Resource Group
- Meaning: A resource group is a logical container in Azure that holds related resources for a solution. It helps organize and manage resources like databases, virtual machines, and networking components.
- Example from your screenshot:
sql_demo_rgCosmoDBWin-ServersNetworkWatcherRG
These are all resource groups that contain other Azure resources.
🔹 Specific Resource Types (e.g., Microsoft.Sql/servers/databases)
- Meaning: These are actual Azure services or components deployed within a resource group. The format follows Azure’s resource provider namespace.
- Examples:
Microsoft.Sql/servers/databases: A SQL database inside a SQL server.Microsoft.Network/networkWatchers: A network monitoring tool.Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks: A virtual network.Microsoft.Compute/disks: A managed disk (often used for VM storage).Microsoft.Network/networkSecurityGroups: A security group controlling inbound/outbound traffic.
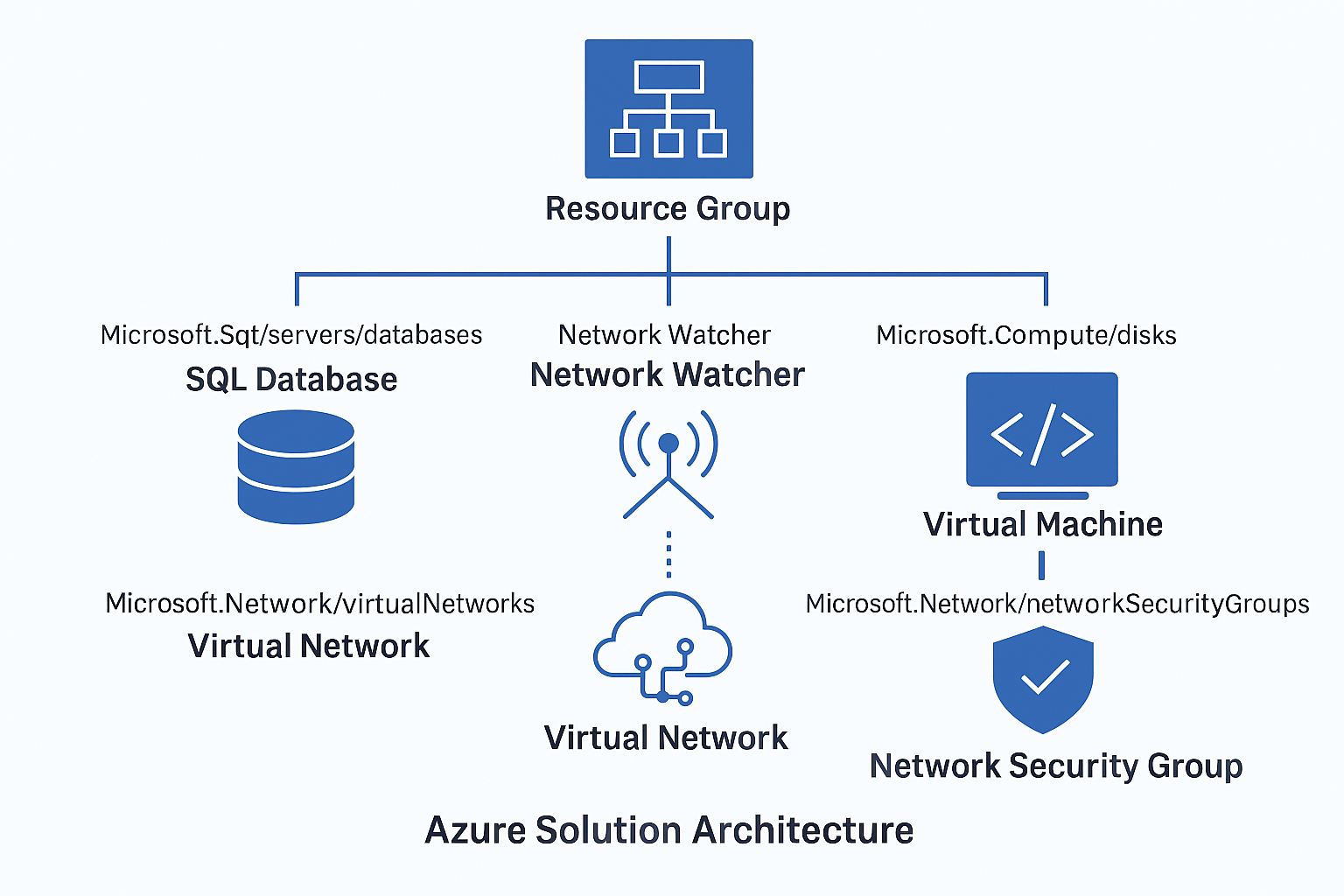
🔐 1. Resource Group (e.g., sql_demo_rg, Win-Servers)
- Role in Architecture: Logical containers for organizing resources by lifecycle, environment (dev/test/prod), or application.
- Access Control: You can assign RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) at the resource group level. This means users can be granted access to all resources within the group without needing individual permissions for each resource.
🗄️ 2. Microsoft.Sql/servers/databases
- Role: Represents SQL databases hosted on Azure SQL servers.
- Access Control:
- You can assign roles like SQL DB Contributor or Reader.
- Fine-grained access can be managed using SQL authentication or Azure AD authentication.
3. Microsoft.Network/networkWatchers
- Role: Tools for monitoring and diagnosing network issues.
- Access Control:
- Typically accessed by network admins.
- Roles like Network Contributor or Reader apply.
🧠 4. Microsoft.Compute/disks
- Role: Managed disks used by virtual machines.
- Access Control:
- Roles like Virtual Machine Contributor or Disk Contributor.
- Important for backup, restore, and performance tuning.
🔌 5. Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces
- Role: Network adapters for VMs.
- Access Control:
- Managed under Network Contributor role.
- Critical for configuring IPs, DNS, and connectivity.
🔒 6. Microsoft.Network/networkSecurityGroups
- Role: Firewall-like rules for controlling traffic to/from resources.
- Access Control:
- Managed by Network Security Group Contributor.
- Essential for enforcing security policies.
🕸️ 7. Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks
- Role: Defines the private network space for Azure resources.
- Access Control:
- Managed by Network Contributor.
- Used for subnetting, peering, and isolation.
How a PAM Uses This:
A PAM product maps these resource types to fine-grained access policies. Instead of giving broad access, it allows just-in-time (JIT) and least privilege access to specific resource types, improving security and compliance.
Summary:
- Resource Group = container for resources.
- Microsoft. types* = actual deployed services/components inside those containers.
Comments are closed